What is Methylene Blue?
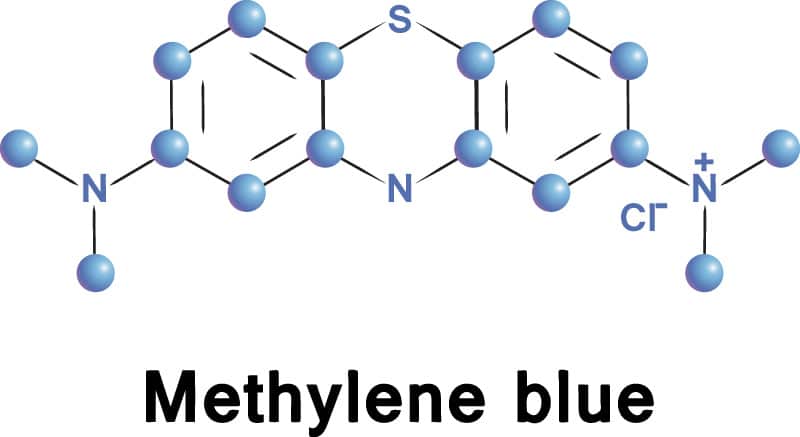
Methylene blue is a century-old drug that was first produced in 1876. It was originally used as clinical medicine to treat various illnesses including malaria, septic shock, cancer chemotherapy, and Alzheimer’s disease. Methylene blue is what is known as a diaminophenothiazine with a low redox potential. This property makes it capable of facilitating electron transport in the mitochondria, which increases ATP production while reducing mitochondrial superoxide production.
Methylene blue (MB), a traditional mitochondrial-targeting antioxidant, showed a potent reactive oxygen species scavenging efficacy in cultured human skin fibroblasts derived from healthy donors and from patients with progeria, a genetic premature aging disease. In comparison with other widely used general and mitochondrial-targeting antioxidants, we found that MB was more effective in stimulating skin fibroblast proliferation and delaying cellular senescence.

Types of Aging
There are two main types of aging that applies to the skin and body as a whole: intrinsic and extrinsic.
Intrinsic
Aging refers to the more or less natural process of aging and physiological changes that occur with time. Examples being the general slowing of the metabolism and inefficient energy production otherwise necessary for skin regeneration.
Extrinsic
Aging refers to epigenetic or environmental factors that can negatively affect the physiology, contributing to aging. Some examples are chronic sun exposure, environmental toxins, and air pollution.
Oxidative stress is the major cause of skin aging that includes wrinkles, pigmentation, and weakened wound healing ability. As such, the application of antioxidants in skin care is well accepted as an effective approach to delay the skin aging process.
Benefits of Methylene Blue
Potential Side Effects
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
- Allergic reactions
- Headaches
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Urine discoloration
- Low blood pressure
